INEB RECENT PUBLICATIONS: “Hippo pathway effectors control cardiac progenitor cell fate by acting as dynamic sensors of substrate mechanics and nanostructure”
INEB researchers have recently published an article in ACS Nano. The article is available online since 7 of February of 2014
Title: “Hippo pathway effectors control cardiac progenitor cell fate by acting as dynamic sensors of substrate mechanics and nanostructure”
Authors: Mosqueira D, Pagliari S, Uto K, Ebara M, Romanazzo S, Escobedo-Lucea C, Nakanishi J, Taniguchi A, Franzese O, Di Nardo P, Goumans MJ, Traversa E, Pinto-do-Ó P, Aoyagi T, Forte G.
Stem cell responsiveness to extracellular matrix (ECM) composition and mechanical cues has been the subject of a number of investigations so far, yet the molecular mechanisms underlying stem cell mechano-biology still need full clarification. Here we demonstrate that the paralog proteins YAP and TAZ exert a crucial role in adult cardiac progenitor cell mechano-sensing and fate decision. Cardiac progenitors respond to dynamic modifications in substrate rigidity and nanopattern by promptly changing YAP/TAZ intracellular localization.
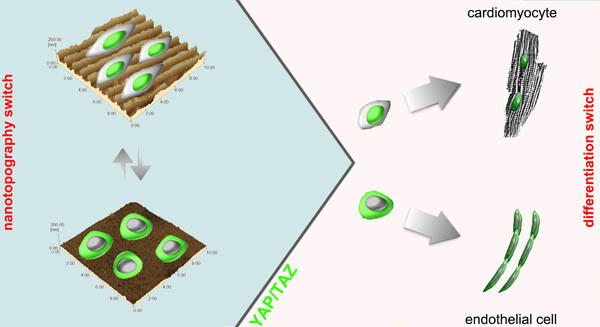
We identify a novel activity of YAP and TAZ in the regulation of tubulogenesis in 3D environments and highlight a role for YAP/TAZ in cardiac progenitor proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, we show that YAP/TAZ expression is triggered in the heart cells located at the infarct border zone. Our results suggest a fundamental role for the YAP/TAZ axis in the response of resident progenitor cells to the modifications in microenvironment nanostructure and mechanics, thereby contributing to the maintenance of myocardial homeostasis in the adult heart. These proteins are indicated as potential targets to control cardiac progenitor cell fate by materials design.
FULL ARTICLE: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nn4058984


