INEB RECENT PUBLICATIONS: Renalase regulates peripheral and central dopaminergic activities
INEB researchers recently published an article in the American Journal of Physiology (Renal Physiology, 308(2): F84-91, 2015), already available. The article is entitled "Renalase regulates peripheral and central dopaminergic activities" and is authored by J. Quelhas-Santos, MP Serrão, I. Soares-Silva, C. Fernandes Cerqueira, L. Simões-Silva, MJ Pinho, F. Remião, B. Sampaio-Maia, GV Desir, and M. Pestana.
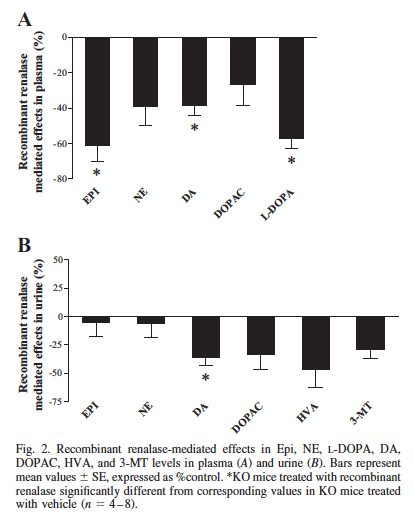
Renalase is a recently identified FAD/NADH-dependent amine oxidase mainly expressed in kidney that is secreted into blood and urine where it was suggested to metabolize catecholamines. The present study evaluated central and peripheral dopaminergic activities in the renalase knockout (KO) mouse model and examined the changes induced by recombinant renalase (RR) administration on plasma and urine catecholamine levels. Our results suggest that the overexpression of L-type amino acid transporter like 1 in the renal cortex of the renalase KO mice might contribute to the enhanced l-DOPA availability/uptake and consequently to the activation of the renal dopaminergic system in the presence of renalase deficiency.


